
MR, Solomon, R, Russell-Bennett & J, Previte 2019, ‘Consumer Behaviour’, 4th Edition, Pearson, Australia. Although they may continue to purchase with the specific brand as it may then satisfy their hedonic needs as they associate positive emotions towards the brands movement. Therefore, consumers may decide to purchase Dove’s products initially to fulfil their utilitarian needs as the products provides them with the function of satisfying personal hygiene needs.

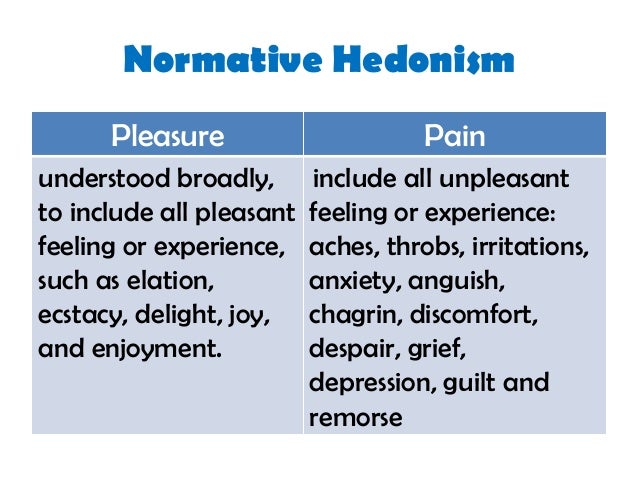
Through the Dove Self-Esteem Project, the Dove logo not only stands for a personal care product but has formed a new meaning of a movement towards building self-esteem and body confidence. ĭove’s advertisements for the Self-Esteem Project Furthermore, the motivating factor behind purchasing products for their symbolism is driven by the product logo. Product symbolism means that consumers are not only purchasing products for their function (utilitarian) but for what they mean to themselves. Through the results of hedonic needs (symbolic meaning or imagery association), this leads to the discussion of product symbolism. This state may lead to symbolic meaning or imagery association to a product or brand. Emotions and feelings such as enjoyment, arousal, curiosity and pleasure are categorised as hedonic needs. Hedonic needs are referred to as an emotional desire. Functionality of a product and the ability of the product make up utilitarian needs. Utilitarian needs are associated with being rational, cognitive and task driven. Two needs that motivate consumers purchases include hedonic needs and utilitarian needs. Although the research is ideal for developing countries that are exploring technological benefits, it is equally important for developed countries for a wider customer reach.Motivation is an internal process that occurs when a consumer realises they have a need that is not satisfied, and they decide to satisfy this need. Implications of the study extend to government policies and economic transformation strategies of the country, while from a theoretical perspective, it contributes towards the better understanding of TPB and TAM. This tendency must be fully exploited by online marketers to not only improve the overall online shopping experience but also to employ user-friendly technology. This implies that online shopping is viewed as an entertaining and fun activity by Malaysian shoppers. A survey analysis from 150 respondents in Malaysia revealed that hedonic motivation is the key attribute that drives consumer satisfaction directly as well as through the mediating role of attitude and perception. We developed a theoretical framework that is informed by the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) and the technology acceptance model (TAM) where customer satisfaction is primarily driven by their attitude and perception, which in turn are driven by risk, utilitarian motivation, as well as hedonic motivation. Abstract : This study examines the antecedents that influence consumer satisfaction towards online shopping in Malaysia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
